Discover the Fascinating World of Velociraptor: Dinosaur Fossil, Cretaceous Habitat, and More!
Scientists are finding more raptor fossils as each year passes. What’s exciting about the fossils is that they are also expanding the knowledge about the raptor dinosaur habitat, fossils giving indications to how these dinosaurs lived. We have seen portrayals of Velociraptors in movies such as Jurassic Park, and it was exciting! As scientists have classified over 40 species of raptor dinosaur of the Dromosauridae family, it makes me wonder, what was the environment these dinosaurs lived in, and how well did they adapt to it?

What Did the Raptor Dinosaur Habitat Look Like?
So, what did the raptor dinosaur habitat look like? It was a desert landscape that was hot, dry, and mountainous with rivers during the late-Jurassic period. The environment was harsh and rugged with little vegetation. Later, in the late Cretaceous period, it was considerably cooler with more vegetation over this type of landscape, such as trees and flowering plants covering the landscape. Raptor fossils have been found in North America, Mongolia, China, and Russia. Velociraptors, in particular, roamed Mongolia, China, and Russia.
The raptors that were found predominantly in the late-Cretaceous period were Velociraptors. Other raptors which I will discuss, lived up until the late-Cretaceous period.
During the Late Cretaceous Period, Velociraptor inhabited Mongolian Desert regions. The semi-arid climate of this desert shaped Velociraptor’s adaptive behaviors. Deinonychus roamed forests and coastal plains of North America. These varied “Climate Conditions” dictated the survival strategies of Deinonychus. Dromaeosaurus dominated the open plains and river valleys.
Dense “Flora” in these areas provided cover for prey and predators alike. Raptors utilized nesting grounds within the continental interiors for reproduction. “Continental Interiors” offered vast expanses for raptors to expand their ranges.
Table of Contents
The Hell Creek Formation, a fossil-rich area, demonstrates raptor habitat diversity. This formation confirms the presence of raptors in subtropical landscapes. The Gobi Desert, known for Velociraptor fossils, represents a unique raptor habitat.
The desert’s arid conditions reveal raptors’ ecological flexibility. The Judith River Formation adds to raptor habitat understanding. This formation provides evidence of ample “Flora” supporting raptor food chains. The Horseshoe Canyon Formation, rich in dinosaur fossils, indicates a dynamic ecosystem.
Resources in this ecosystem were vital for raptor subsistence. Lastly, the Iren Dabasu Formation shows raptor adaptations to inland environments. In this formation, raptors likely encountered a variety of “Climate Conditions,” from seasonal variations to climatic shifts.
From the late-Jurassic until the mass extinction in the late-Cretaceous, it spans some 88 million years, so what we know about raptors, its habitat, and behavior is only from the fossils we have found and studies that paleontologists have done with those fossils. Nevertheless, what we currently do know about raptors is fascinating. Now that we have a general idea of what the raptor dinosaur habitat looked like for raptors, there are other things that we can explore about raptors. Let’s take a closer look.
Types of Raptor Dinosaurs
#1. There Were Hundreds of Species of Raptor
As raptors lived over some 88 million years, there is likely to have been hundreds if not thousands of related species. Unfortunately, we have only a part of the whole picture with only about 40 classified into families and clades, and paleontologists continue to find new raptor fossils with each year that passes.

The table below is just a snapshot of some of the raptor species that existed. I list the raptor in the first column, then a short description in the second column and finally, in the third column, I state where the raptor’s fossils are found.
Table 1 - List of 10 Types of Raptors
| Raptor Dinosaur Name | Classification and Description | Where Fossils Found |
|---|---|---|
| Buitreraptor | A small raptor dinosaur thought to hunt lizards and small mammals. Lived during the Cretaceous period | South America |
| Bambiraptor | A small raptor dinosaur, it was a bird-like raptor dinosaur and the fossil skeleton is 95% complete | North America |
| Tianyuraptor | Considered a transitional species of bird, this raptor dinosaur lived in the early Cretaceious | China |
| Changyuraptor | The largest "four-winged" raptor dinosaur. Lived in the early Cretaceous period | China |
| Velociraptor | It was a rather small raptor. Lived in the late Cretaceous period | Mongolia |
| Deinonychus | Known as the dinosaur that changed the way scientists thought about dinosaurs- being warm-blooded. Lived in the late Cretaceous | North America |
| Utahraptor | One of the largest raptor dinosaurs in North America, it lived in the late Cretaceous | North America |
| Achillobator | One of the largest known raptors. Lived during the late Cretaceous | Mongolia |
| Halszkaraptor | Only one species of this raptor dinosaur. Found evidence it lived close to water | Mongoila |
| Dakotaraptor | Smaller than Utahraptor, this raptor dinosaur lived at the very end of the Mesozoic era. | North America |
| Raptor Dinosaur Name | Classification and Description | Where Fossils Found |
How Did a Raptor Look Like? How Tall is a Raptor Dinosaur?
#2 What Did Raptors Look Like? Some Features:
- Head – They had crocodile-like snouts (not beaks) with sharp, serrated teeth on the jaws. The jaws could snap shut fast and tear chunks of meat from the prey.
- Legs – Raptors were dinosaur therapods, a species that walked on its hind legs, which had three-fingered claws.
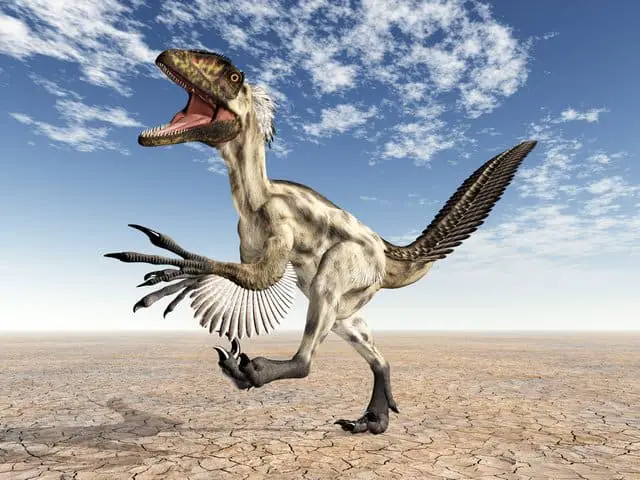

- Feathers – There is fossil evidence now that suggests that many of the raptors had feathers covering most, if not all, of its body. While no actual raptor feathers have been found, the quill impressions are left as well as some coloring, which indicates to scientists that these dinosaurs had feathers.
- Claws – The claw of the raptor was three-fingered. They were raised and curved, which made them more deadly. These were deadly attacking weapons that could slash and injure prey. They were also useful for protection and defense when fighting.
- Tail and Tail Feathers – It relied on its stiff tail for maintaining balance while in motion. As mentioned above, they most likely had feathers, and feathers on the tail could be used to add weight and balance further.
- Warm-Blooded or Cold-Blooded? – Scientists believe that velociraptors were warm-blooded like modern-day birds. In that perspective, the raptors were even more deadly hunters that could regulate their body temperatures. Therefore, their warm-blooded nature aided them in pursuing prey actively and mauling them despite the weather.
- How fast and agile were Velociraptors? – Despite being small, Velociraptors were very fast and agile.
- How much did Velociraptors weigh? -Velociraptors weighed 55 pounds.
- How long were Velociraptors? – Velociraptors were 1.8 meters (6 feet) in length.
#3 Raptor Height
On average a raptor stood approximately 6.5 ft tall (198 cm) to 23 ft long (7 meters). Velociraptors were considerably smaller than depicted in movies. Velociraptors were only a bit taller than a modern-day turkey or a crane, based on the fossils we have found. They were 1.6 ft tall and 6.5 ft long and weighed about 30 lbs (13.2 kg), and their bodies were adapted to fast, light mobility.
Despite being small, it could move fast. Nonetheless, this crane or turkey-sized predator was one of the most dangerous during the Mesozoic period.
Raptors Were Predators and Also Were Hunted
#4 -Raptors Were Hunted By Other Predators and Sometimes Stole or Scavenged Meat From Other Larger Predators
Raptors were carnivorous, meaning they were meat-eating predators that hunted other dinosaurs. These dinosaurs were skillful and efficient predators. They often targeted prey that was smaller than them, but they could target far bigger animals than them.

It all depended on their age, size, and companionship that they kept. Raptors had sharp teeth and clutching arms. However, their talon-like, curved claws served as dangerous stabbing and slashing weapons that could sink and anchor into flesh and bones.
As good as they were as predators, they also were considerably smaller in size, and this meant that there was a threat of being hunted and killed by other more massive dinosaurs. Another way they might run into trouble with a larger predator is if they scavenged meat from them, and get into a fight over it.
How Fast Could Raptors Run in the Raptor Dinosaur Habitat? How Smart Were Velociraptors?
#6 The Fastest Raptors?
Raptors could achieve speeds of up to 25 miles per hour (40.23 km per hour). Despite being feathered and light-boned, raptors couldn’t outrun some species such as the T-rex, Gallimimus, or their relatives Ornithomimus and Struthiomimus. Of all the raptors, it’s estimated that the Utahraptor was perhaps the fastest raptor.
Velociraptors, in particular, were not the fastest raptors dinosaurs of the Cretaceous period, but they were considerably speedier and more agile than most. Why did they earn the Latin connotation of “speedy thieves” if they weren’t the fastest predators? It has to do with their relatively small sizes and suspected aggressive hunting techniques. In reality, these dinosaurs were considered “speedy thieves” because they had more balance and could jump and dodge over obstacles better than other predators.
————————————————————————————————
Related Dinosaur Articles You Might Also Be Interested In:
Herbivore Dinosaurs – What’s So Cool About Them? (Types, Sizes, Facts)
The 13 Best-Known, Most-Loved Dinosaurs and Why
What Are Long Neck Dinosaurs (Types, Size, List)?
————————————————————————————————
#7 Raptors Had Agility and Ability to Sprint and Jump –
For starters, raptors could chase smaller prey with more balance than bigger dinosaurs. With the raptors dinosaur habitat described above, they were well suited for this environment. They could navigate past obstacles while running full speed and even flexibly jump when going for the kill. They were considerably agile and could launch successful attacks, especially with their feathered, mid-stride flights.
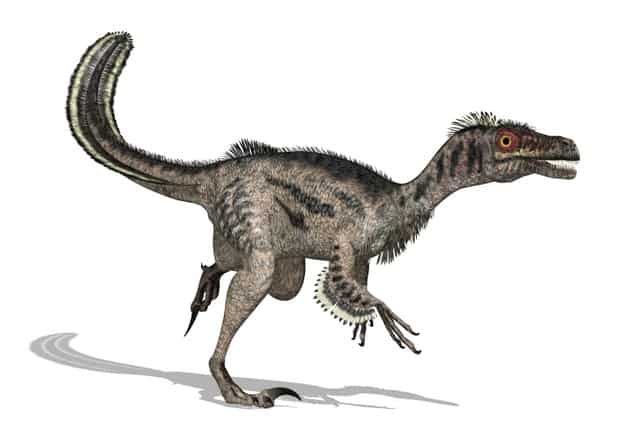
#8 How Do Velociraptors Compare to Jurassic Park Movies
The Jurassic Park movie went a long way to create a cool, awesome looking raptor dinosaur habitat and island habitat for dinosaurs. However, there were some creative liberties taken with how they portrayed raptors. The raptors that you saw on Jurassic Park were about five times the size of real raptors, and they were actually from a related species, the Deinonychus. Nevertheless, it was fantastic entertainment. Let’s take a look at how some of the entertainment in Jurassic Park’s depictions of raptors compare to what scientists have found.
Table 2 - Comparison Table - Jurassic Park and Raptor Fossil Science
| Comparison Topic | How the Raptor Was Portrayed in Jurassic Park Movies | Raptor Fossil Science Indicate | Creativity Level (scale of 1-5) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dinosaur referenced | Velociraptor | Best fossil match - Deinonychus | 4 |
| Intelligence | Velociraptors were smart and intelligent | They were smart, but not the smartest | 4 |
| Size | The Velociraptor was about 5-7ft | Fossils indicate 2 ft in height | 3 |
| Hunting in Packs | Velociraptors hunted in packs | No proof they hunted in packs | 3 |
| Pack intelligence and communication | Velociraptors could communicate with each other and had pack intelligence | No proof that they communicated, although birds can communicate with each other | 4 |
| Feathers | They didn’t have feathers | They had feathers | 4 |
| Time period | Jurassic Park implies Jurassic time period | Velociraptors lived the late Cretaceous | 1 |
| Comparison Topic | How the Raptor Was Portrayed in Jurassic Park Movies | Raptor Fossil Science Indicate | Creativity Level (scale of 1-5) |
#9 Can Raptors Swim?
Raptors lived near rivers and streams, but probably could not swim or stay in water for any length of time. As mentioned above, the raptors dinosaur habitat was hot and dry during the late-Jurassic and then cooled towards the late-Cretaceous. The hunting raptors dinosaurs lived in desert environments and were adapted to scorching environments.
For these raptors, it seldom ever had to get into the water. Nonetheless, most vertebrates can survive a short dip in water even though they cannot swim. If you drop an elephant into a lake or pond, it could float and move long enough to get out successfully. It is thought that raptors hunted near watering holes, but probably didn’t choose to be in the water.
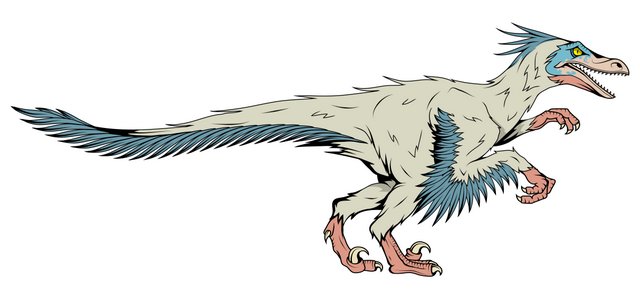
How Smart Were Raptors? How Smart Is a Velociraptor?
#10 Raptors Were Not Very Intelligent
Although not very intelligent, they were some of the smartest dinosaurs of all time. Their brain capacity, relative to their sizes, was tremendous, making them considerably smarter than others. How smart they were, in reality, is something we may never be able to determine.
The reputation of raptors out in the public (due in large part because of the movies) suggests that raptors were intelligent and aggressive. They are assumed to have crept up on prey and driving targets out of protective herds.
There is no proof of these assumptions and unfortunately, the fossils do not give enough information on habits and group habits of raptors.
Raptor Enemies and Did Velociraptors Hunt in Packs?
#11 Raptor’s Enemies
Raptors May Have Been Hunted by Bigger Predators – Raptors were rather small and had to run away from bigger dinosaurs that were aggressive. Bigger predators such as Tarbosaurus, a carnivore existing in the late-Cretaceous period, may have preyed on raptors. Additionally, large, armored herbivores like Triceratops or Styracosaurus didn’t like predators and may have actively pursued raptors if they got too close.
Regarding Velociraptors, there is a fantastic fossil found of a Velociraptor and a Protoceratops, that died soon after their battle. The Protoceratops is a small pig-sized herbivore, and it seems to have inflicted severe wounds on the attacking Velociraptor.
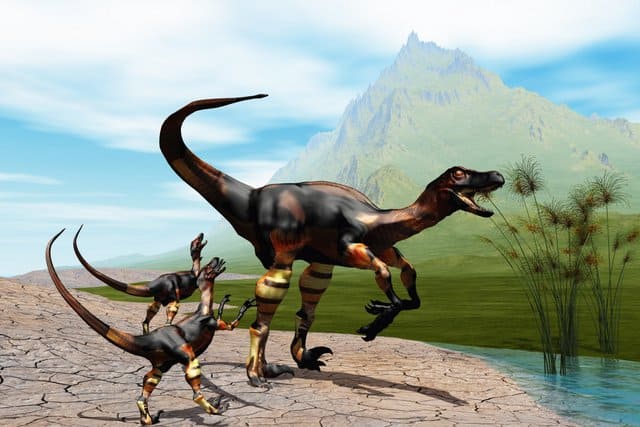

#11 Raptors and Velociraptors May Have Hunted in Packs
They attacked relatively smaller and younger dinosaurs. Some scientists suggest that they did hunt in packs, surrounding the prey and inflicting multiple wounds until the dinosaur dies. With multiple attacks, it could easily overcome even larger dinosaurs.
However, some scientists have lately stated that there is no direct evidence that raptors hunted in packs. Instead, an individual raptor would sneak up on prey, and after injuring them, wait for the attacked victim to bleed and die before going back to eat it. The behavior is similar to Komodo dragons, whose bite is full of bacteria, and then devours the prey after it dies.
Thinking of why a Velociraptor was named in such a way gives some interesting correlations. Velociraptor’s connotation of being “speedy thieves” perhaps comes from the nature of their surprise attacks. Not only are these dinosaurs fast, but they likely used the element of surprise. Still, they couldn’t use it on somewhat larger prey unless they had the advantage of numbers.
Comparison of The Jurassic Park and Raptor Fossil Science
According to Jurassic Park movies, Velociraptors were depicted as highly intelligent creatures, capable of communication and exhibiting pack hunting behavior. However, raptor fossil science indicates that while they were indeed intelligent, they may not have been the smartest among dinosaurs. Additionally, the fossils suggest a smaller size, with a height of around 2 feet, which is in contrast to the larger portrayal in the movies.
| Comparison Topic | How the Raptor Was Portrayed in Jurassic Park Movies | Raptor Fossil Science Indicate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Creativity Level (scale of 1-5) | Dinosaur referenced | Velociraptor | Best fossil match | Deinonychus | |
| 4 | Intelligence | Velociraptors were smart and intelligent | They were smart, but not the smartest |
| 3 | Size | The Velociraptor was about 5-7ft | Fossils indicate 2 ft in height |
| 3 | Hunting in Packs | Velociraptors hunted in packs | No proof they hunted in packs |
| 4 | Pack intelligence and communication | Velociraptors could communicate with each other and had pack intelligence | No proof that they communicated, although birds can communicate with each other |
| 4 | Feathers | They didn’t have feathers | They had feathers |
| 1 | Time period | Jurassic Park implies Jurassic Time period | Velociraptors lived the late Cretaceous |
Fossils of the Velociraptor – Where They Were Found
According to various paleontological findings, raptor fossils, including those of Velociraptors, have been discovered in multiple regions. These regions include North America, Mongolia, China, and Russia. In particular, it has been observed that Velociraptors roamed the vast landscapes of Mongolia, China, and Russia, showcasing their wide distribution across these areas.
Adding to this knowledge, it is worth noting that the Gobi Desert holds a significant place in paleontological history. The first dinosaur skeleton ever discovered, believed to be a Velociraptor, was found within the vast expanse of the Gobi Desert.
This finding suggests that Velociraptors were indeed present and inhabited the Gobi Desert, contributing to the rich diversity of dinosaur fossils found in this region. Therefore, while Velociraptors are known to have existed in the Gobi Desert based on the discovery of the first dinosaur skeleton, it is important to acknowledge their presence in other regions as well.
Fossils found in North America, Mongolia, China, and Russia indicate that Velociraptors were not limited to a single location but rather inhabited a broader range of territories, showcasing their adaptability and widespread distribution during the prehistoric era.
Velociraptor Characteristics
Velociraptors, in particular, were not the fastest raptor dinosaurs of the Cretaceous period, but they were considerably speedier and more agile than most. They earned the Latin connotation of ‘speedy thieves’ due to their relatively small sizes and suspected aggressive hunting techniques. However, there is much more to their characteristics that make them fascinating creatures. The Velociraptor habitat was complimentary to its physical features,
Velociraptors possessed very powerful back legs with long claws that could rip into their prey. These claws were lifted back when they were running, showcasing their remarkable agility. While they may not have been the fastest predators, they had exceptional balance and the ability to jump and dodge over obstacles better than other predators.
Their smaller size allowed them to chase smaller prey with more precision and balance. The raptor dinosaur habitat described above perfectly suited their hunting abilities, enabling them to navigate past obstacles while running at full speed and even flexibly jump mid-stride when going for the kill. In addition to their physical attributes, Velociraptors had a unique three-fingered structure, setting them apart from other dinosaurs with different finger configurations.
This characteristic contributed to their gripping capabilities, allowing them to firmly grasp their prey. Velociraptors lived about 75 to 71 million years ago during the Cretaceous period, alongside some of the most renowned meat-eating dinosaurs such as the T. Rex and Albertosaurus. This timeframe provides important context for understanding their place in prehistoric ecosystems and their interactions with other species.
Another fascinating aspect of Velociraptors is their intelligence. They possessed a relatively large brain, which enhanced their agility and problem-solving abilities. This intelligence also enabled them to hunt together in packs, making them fearsome predators. Working cooperatively, they could strategize and execute successful attacks on their prey. Escaping their coordinated assault would have been a nearly impossible feat.
Furthermore, it is worth noting that Velociraptors exhibited feathered, mid-stride flights. This feathered adaptation allowed them to further enhance their agility and maneuverability during hunts. In conclusion, Velociraptors were not only known for their speed and agility but also possessed a range of other remarkable characteristics.
Their powerful back legs, long claws, three-fingered structure, intelligence, and ability to hunt together in packs made them formidable and adaptable predators. These fascinating traits, combined with their feathered flights, paint a comprehensive picture of the unique and awe-inspiring nature of Velociraptors.
Parting Shot
In many ways, raptors were an exciting species. The Jurassic Park movies have given the inspiration to see these dinosaurs in a full environment and habitat, even with behaviors and personality. As we learn more about these dinosaurs from a scientific perspective, solving the puzzles that are before us when we find raptor fossils, it is just as exciting to put the puzzle pieces together.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Some Interesting Facts About the Velociraptor’s Habitat?
The Velociraptor, specifically the Velociraptor mongoliensis, lived in what is now known as the Gobi Desert in Mongolia. This area was a sandy dune desert with scattered trees. Fossils have also been found in other parts of Northern China. The habitats date back to around 75 million years ago, towards the end of the Cretaceous period.
What Is a Velociraptor?
A velociraptor is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 75 million years ago. Velociraptor mongoliensis, the species most are familiar with, was about the size of a large turkey. They were bipedal, meaning they walked on two legs, and their long tail provided balance. The most known feature of a velociraptor is their large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot, which they presumably used for predatory behavior.
What Is the Pronunciation of Velociraptor?
The correct pronunciation of Velociraptor is “vell-os-eeraptor.”
What Is the History of Velociraptor Discovery?
The first velociraptor fossil was discovered in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia by a team of paleontologists from the American Museum of Natural History in 1923. The fossil was named the type species V. mongoliensis in 1924. Another species, V. osmolskae, was discovered in Inner Mongolia, Northern China in 2008.
What Is the Meaning of The Name “Velociraptor”?
The name velociraptor comes from the Latin words for swift and robber or plunderer. This name was chosen to reflect the speed, agility, and predatory behavior exhibited by these reptiles in their natural habitats.
Why Are Velociraptors Believed to Have Feathers?
Many paleontologists believe that Velociraptors, like many theropod dinosaurs, had feathers. The reason for this belief lies in a fossil found in 1998 of a smaller relative dinosaur species, the Sinornithosaurus milleni. This fossil preserves a Velociraptor-like dinosaur with clear feather impressions, suggesting that other relatives like the Velociraptor also had feathers.
When Was the Velociraptor Popularized?
The Velociraptor gained wider recognition and popularity with the public through its depiction in the 1993 movie Jurassic Park, even though the velociraptors in the movie were significantly larger and lacked feathers unlike their real-life counterparts.
Are There Any Other Species of Velociraptor?
Yes, aside from the Velociraptor mongoliensis, another species known as Velociraptor osmolskae was discovered in 2008 in Inner Mongolia, Northern China. These are the two confirmed species within the Velociraptor genus but there might be more waiting to be discovered.
Where Have Most Velociraptor Fossils Been Found?
Most velociraptor specimens have been discovered in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia. Some have also been found in Northern China, specifically Inner Mongolia. Two sites, the Djadochta Formation in Mongolia and the Bayan Mandahu Formation in Inner Mongolia, are particularly rich in velociraptors and other dinosaur fossils.
How Big Was a Velociraptor?
Despite depictions in popular media, velociraptors were not very large. They were about the size of a large turkey, standing at around 0.5 meters tall at the hips and measuring up to 2 meters long, including their long tail. However, they were likely fast and agile predators despite their small stature.
What Kind of Diet Did Velociraptors Have?
Velociraptors were carnivores. They likely preyed on smaller animals, using their speed, agility, and the large, sickle-shaped claw on each foot to hunt. Their teeth were sharp and serrated, perfect for ripping into the flesh of their prey.
